解析库与Beautiful Soup 通过request库,我们已经能够抓取网页信息了,但要怎么提取包含在Html代码里面的有效信息呢?谈到匹配有效信息你肯定会想到正则表达式,这里就不讨论了,实际上关于正则表达式已经可以写一本书了,并且由于网页特殊的层级结构,也没必要使用正则表达式。python提供更好用的html和xml的解析库Beautiful Soup 和XPath等。
什么是Beautiful Soup Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会帮你节省数小时甚至数天的工作时间
———Beautiful Soup中文文档
安装 1 2 pip3 install beautifulsoup4
学习准备 为了学习和测试Beautiful Soup,我写了一个简单的程序框架,包含3个函数获取页面,解析页面,和主函数,测试的时候只要修改解析函数的部分代码就可以了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupdef getHtml (url) : try : r = requests.get(url,timeout = 30 ) r.encoding = r.apparent_encoding; return r.text except : return "" def soupHtml (html) : print(html) soup = BeautifulSoup(html,'lxml' ) if __name__ == '__main__' : url = "http://www.baidu.com" html = getHtml(url) soupHtml(html)
可以看到爬取的是百度的首页,之后的代码,添加进去就能运行了
基本用法 1 2 BeautifulSoup (content,"html.parser" /"lxml" )
两个参数cnetent表示待解析的网页内容,后面的参数可以理解为待解析的格式。lxml解析器有解析HTML和XML的功能,而且速度快,容错能力强,所以推荐使用它。
选择元素 根据标签名来选择元素
1 2 3 4 5 6 soup = BeautifulSoup(html ,'lxml' ) print (soup.title) print (soup.head) print (soup.div) >>> <title>百度一下,你就知道</title>
连带标签一起输出,当有多个标签匹配时,只返回第一个
获取内容 标签的string方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 soup = BeautifulSoup(html ,'lxml' ) print (soup.title.string) print (soup.head.string) print (soup.div.string) >>> 百度一下,你就知道
获取标签的属性 html中的标签有很多属性,例如,id,name,class,href等等,可以通过attrs 获取标签的属性
1 2 3 4 5 soup = BeautifulSoup(html ,'lxml' ) print (soup.link.attrs) >>> {'rel' : ['stylesheet' ], 'type' : 'text/css' , 'href' : 'http://s1.bdstatic.com/r/www/cache/bdorz/baidu.min.css' }
获取属性的值 通过返回的值,可以知道它是字典类型的结构,这样就可以通过键获取他的值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 soup = BeautifulSoup(html ,'lxml' ) print (soup.p) >>> <p id="lh" ><a href="http://www.baidu.com/cache/sethelp/help.html" target="_blank" >把百度设为主页</a><a href="http://home.baidu.com" >关于百度</a><a href="http://ir.baidu.com" >About Baidu</a></p> print (soup.p.attrs) >>> {'id' : 'lh' } print (soup.p.attrs['id' ]) >>>lh
关联选择 在做选择的时候,有时候不能做到一步就选到想要的节点元素,需要先选中某一个节点元素,然后以它为基准再选择它的子节点、父节点、兄弟节点等
1.子节点和子孙节点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for i,content in enumerate(soup.head.contents): print(i,content) for i,child in enumerate(soup.head.children): print(i,child) >>>0 <meta content ="text/html;charset=utf-8" http-equiv ="content-type" /> 1 <meta content ="IE=Edge" http-equiv ="X-UA-Compatible" /> 2 <meta content ="never" name ="referrer" /> 3 <title > 百度一下,你就知道</title > 4 <style > html ,body {height :100% }html {overflow-y :auto}body {font :12px arial;background :#fff }body ,p ,form ,ul ,li {margin :0 ;padding :0 ;list-style :none}body ............
输出head标签的子节点,contents和children是等效的
如果要得到所有的子孙节点的话,可以调用descendants属性
1 2 3 4 for i ,child in enumerate(soup.body .descendants ): print(i ,child)
2.父节点和祖先节点 如果要获取某个节点元素的父节点,可以调用parent属性,获取其祖先节点调用其parents属性。
3.兄弟节点 next_sibling和previous_sibling分别获取节点的下一个和上一个兄弟元素,next_siblings和previous_siblings则分别返回所有前面和后面的兄弟节点的生成器。
查询方法 1.find_all() find_all查询所有符合条件的元素。给它传入一些属性或文本,就可以得到符合条件的元素了。
API接口如下:
1 2 3 find_all(name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 for i,input in enumerate(soup.fiind_all(name ='input' )): print (i,input) >>> 0 <input name ="bdorz_come" type ="hidden" value ="1" /> 1 <input name ="ie" type ="hidden" value ="utf-8" /> 2 <input name ="f" type ="hidden" value ="8" /> 3 <input name ="rsv_bp" type ="hidden" value ="1" /> 4 <input name ="rsv_idx" type ="hidden" value ="1" /> 5 <input name ="tn" type ="hidden" value ="baidu" /> 6 <input autocomplete ="off" autofocus ="" class ="s_ipt" id ="kw" maxlength ="255" name ="wd" value ="" /> 7 <input class ="bg s_btn" id ="su" type ="submit" value ="百度一下"
找出所有的input标签
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 for i ,tag in enumerate(soup.find_all(attrs={'class' :'mnav' })): print(i ,tag) >>> 0 <a class="mnav" href="http://www.nuomi.com" >糯米</a> 1 <a class="mnav" href="http://news.baidu.com" >新闻</a> 2 <a class="mnav" href="http://www.hao123.com" >hao123</a> 3 <a class="mnav" href="http://map.baidu.com" >地图</a> 4 <a class="mnav" href="http://v.baidu.com" >视频</a> 5 <a class="mnav" href="http://tieba.baidu.com" >贴吧</a> 6 <a class="mnav" href="https://passport.baidu.com/v2/?login&tpl=mn&u=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.baidu.com%2F" >登录</a> 7 <a class="mnav" href="http://www.baidu.com/gaoji/preferences.html" >设置</a>
找出所有class属性为”mnav”的标签
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 import re# 导入正则匹配库 print (soup.find_all(text =re.compile('百' )))['百度一下,你就知道' , '把百度设为主页' , '关于百度' , '使用百度前必读' ]
2.find() find()方法与find_all(),方法一致,只是find()返回的是单个元素,也就是第一个匹配的元素,而前者返回的是所有匹配的元素组成的列表。这里就不讨论了
CSS选择器 就是专门用于筛选指定样式的标签,通过select方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 print (soup.select('.mnav' ) for i ,tag in enumrate(soup.select('.mnav' )): print(i ,tag) >>>0 <a class="mnav" href="http://news.baidu.com" name="tj_trnews" >新闻</a> 1 <a class="mnav" href="http://www.hao123.com" name="tj_trhao123" >hao123</a>2 <a class="mnav" href="http://map.baidu.com" name="tj_trmap" >地图</a>3 <a class="mnav" href="http://v.baidu.com" name="tj_trvideo" >视频</a>4 <a class="mnav" href="http://tieba.baidu.com" name="tj_trtieba" >贴吧</a>
通过结果我们发现其实完全可以通过class属性来查找,应为通过CSS来查找本质就是通过class属性来查找
程序实现 爬取最好大学网2018年排名信息,并格式化输出
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 <tbody class "hidden_zhpm" style="text-align: center;" > <tr class "alt" > <td> 1 </td> <td> <div align="left"> 清华大学 </ div> </td> <td> 北京 </ td> <td> 95.3 </td> <td class="hidden-xs need-hidden indicator5"> 100.0 </ td>
1.所有大学信息包含在tbody 的子标签中,即整个表格
2.每一所大学在一个tr 标签中,即表格中的一行
3.各大学的排名,名称,综合评分,在td 标签中,即表格的一列
request + BeautifkuSoup实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 import requestsfrom bs4 import BeautifulSoupimport bs4def getUnivtext (url) : try : r=requests.get(url,timeout=30 ); r.raise_for_status() r.encoding=r.apparent_encoding; return r.text except : return "" def fillUnivList (ulist,html) : soup=BeautifulSoup(html,"html.parser" ) for tr in soup.find('tbody' ).children: if isinstance(tr,bs4.element.Tag): tds=tr('td' ) ulist.append([tds[0 ].string,tds[1 ].string,tds[3 ].string]) def printUnivList (ulist,num) : print("{:^10}\t{:<10}\t{:<10}\t" .format("排名" ,"大学名称" ,"评分" )) for i in range(num): u=ulist[i] print("{:^10}\t{:^6}\t{:^10}\t" .format(u[0 ],u[1 ],u[2 ])) if __name__ == '__main__' : Uinfo=[] url="http://www.zuihaodaxue.com/zuihaodaxuepaiming2018.html" html=getUnivtext(url) fillUnivList(Uinfo,html) printUnivList(Uinfo,310 )
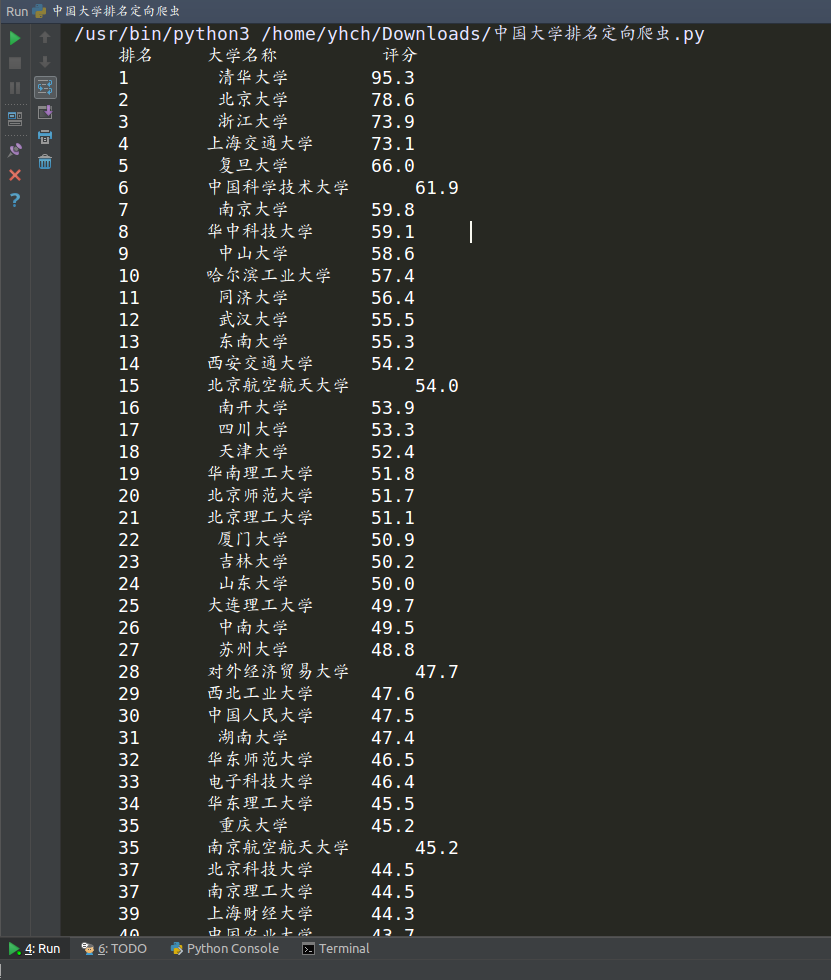
运行效果
投喂我 写文不易,如果本文对你有帮助,点击Donate,微信和支付宝投喂我